React JS
React is an open-source
JavaScript library for building user interfaces or UI components.
It was created at Facebook and open-sourced in March of 2013. It is used
on social platforms like Instagram, Facebook, Twitter. And It is used on content
delivery platforms like NetFlix, Spotify.
Beyond Web applications,
you can create native mobile applications using React Native.
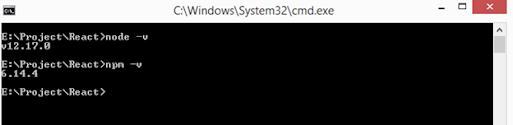
Check your system node and
npm version. Node version should be greater than 8.10 and for npm, we need
version 5.6.
Create a new React-app:
Command to create a new
react app: npx create-react-app new-app
To start the react app: npm start
Folder Structure:
package.json – It contains all the project dependencies.
src folder – It contains the files required to build the application
public folder – when we ready to build the app for production all the
built files will be placed in the public folder.
Create a React element:
Elements are the building
blocks of React apps. We can create a new element in the UI by using React.createElement() and pass this to ReactDOM.render()
which renders an element in the page.
ReactDOM.render() takes two arguments.
First – the element that we
want to create
Second – where we want to
render the element.
React.createElement()
– takes three arguments
First – the name of the tag
that we want to create,
Second – the properties of
the element,
Third - the children tag or it could be some text.
In the above code, we are
creating the “h1” element and
rendering it to the “root” element.
Where is the root element?
We can find it in the index.html file in the public folder.
In the
React.createElement(), we can apply properties to the element as an
object.




Comments
Post a Comment